Log custom LLM traces
Nothing will break if you don't log LLM traces in the correct format and data will still be logged. However, the data will not be processed or rendered in a way that is specific to LLMs.
The best way to logs traces from OpenAI models is to use the wrapper available in the langsmith SDK for Python and TypeScript. However, you can also log traces from custom models by following the guidelines below.
LangSmith provides special rendering and processing for LLM traces, including token counting (assuming token counts are not available from the model provider) and token-based cost calculation. In order to make the most of this feature, you must log your LLM traces in a specific format.
Chat-style models
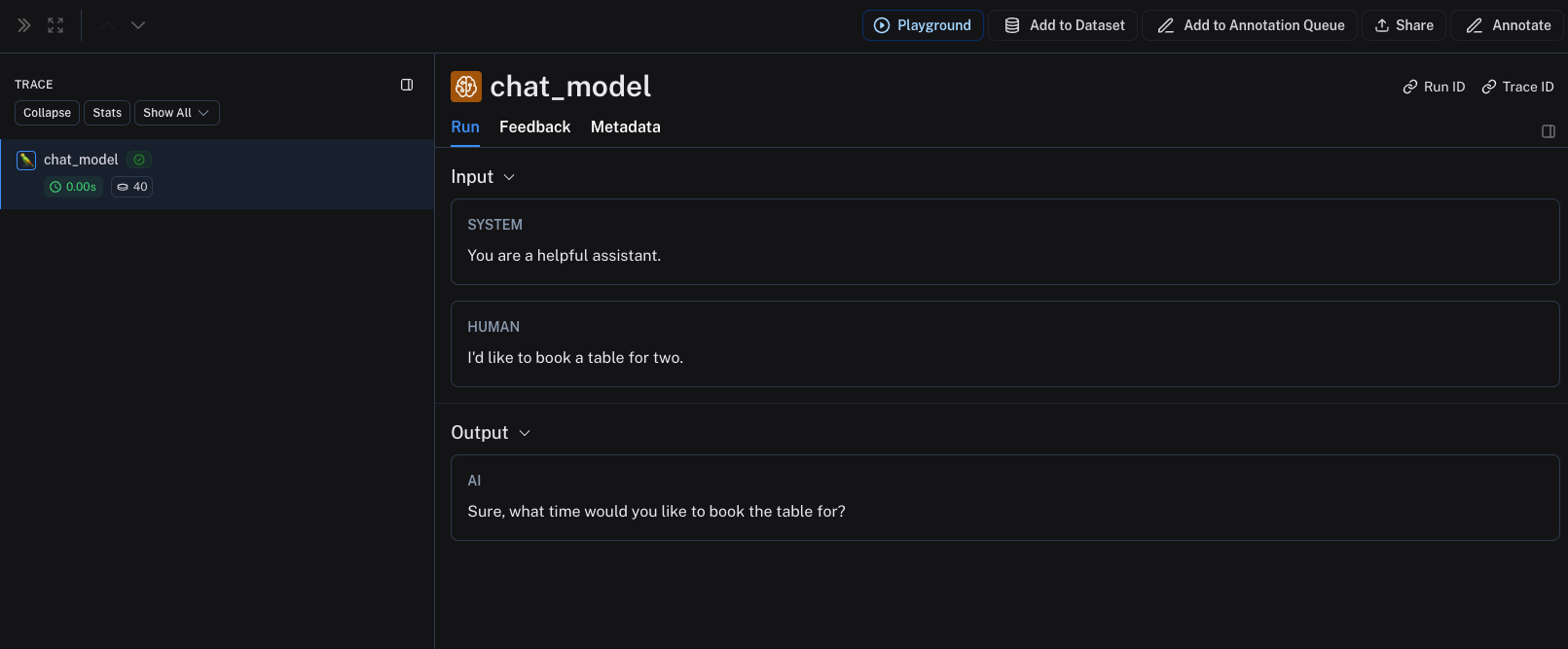
For chat-style models, inputs must be a list of messages in OpenAI-compatible format, represented as Python dictionaries or TypeScript object. Each message must contain the key role and content.
The output is accepted in any of the following formats:
- A dictionary/object that contains the key
choiceswith a value that is a list of dictionaries/objects. Each dictionary/object must contain the keymessage, which maps to a message object with the keysroleandcontent. - A dictionary/object that contains the key
messagewith a value that is a message object with the keysroleandcontent. - A tuple/array of two elements, where the first element is the role and the second element is the content.
- A dictionary/object that contains the key
roleandcontent.
The input to your function should be named messages.
You can also provide the following metadata fields to help LangSmith identify the model and calculate costs. If using LangChain or OpenAI wrapper, these fields will be automatically populated correctly. To learn more about how to use the metadata fields, see this guide.
ls_provider: The provider of the model, eg "openai", "anthropic", etc.ls_model_name: The name of the model, eg "gpt-3.5-turbo", "claude-3-opus-20240307", etc.
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import traceable
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."},
]
output = {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
]
}
# Can also use one of:
# output = {
# "message": {
# "role": "assistant",
# "content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
# }
# }
#
# output = {
# "role": "assistant",
# "content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
# }
#
# output = ["assistant", "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"]
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def chat_model(messages: list):
return output
chat_model(inputs)
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "I'd like to book a table for two." }
];
const output = {
choices: [
{
message: {
role: "assistant",
content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
]
};
// Can also use one of:
// const output = {
// message: {
// role: "assistant",
// content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
// }
// };
//
// const output = {
// role: "assistant",
// content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
// };
//
// const output = ["assistant", "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"];
const chatModel = traceable(
async ({ messages }: { messages: { role: string; content: string }[] }) => {
return output;
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "chat_model", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await chatModel({ messages });
The above code will log the following trace:
Stream outputs
For streaming, you can "reduce" the outputs into the same format as the non-streaming version. This is currently only supported in Python.
def _reduce_chunks(chunks: list):
all_text = "".join([chunk["choices"][0]["message"]["content"] for chunk in chunks])
return {"choices": [{"message": {"content": all_text, "role": "assistant"}}]}
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
reduce_fn=_reduce_chunks,
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def my_streaming_chat_model(messages: list):
for chunk in ["Hello, " + messages[1]["content"]]:
yield {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"content": chunk,
"role": "assistant",
}
}
]
}
list(
my_streaming_chat_model(
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please greet the user."},
{"role": "user", "content": "polly the parrot"},
],
)
)
Manually provide token counts
By default, LangSmith uses TikToken to count tokens, utilizing a best guess at the model's tokenizer based on the ls_model_name provided. Many models already include token counts as part of the response. To send them to LangSmith, you can add a usage_metadata key to the function's response, containing a dictionary with the keys input_tokens, output_tokens and total_tokens.
If using LangChain or OpenAI wrapper, these fields will be automatically populated correctly.
- Python
- TypeScript
from langsmith import traceable
inputs = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to book a table for two."},
]
output = {
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?"
}
}
],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 27,
"output_tokens": 13,
"total_tokens": 40,
},
}
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def chat_model(messages: list):
return output
chat_model(inputs)
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "I'd like to book a table for two." },
];
const output = {
choices: [
{
message: {
role: "assistant",
content: "Sure, what time would you like to book the table for?",
},
},
],
usage_metadata: {
input_tokens: 27,
output_tokens: 13,
total_tokens: 40,
},
};
const chatModel = traceable(
async ({
messages,
}: {
messages: { role: string; content: string }[];
model: string;
}) => {
return output;
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "chat_model", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await chatModel({ messages });
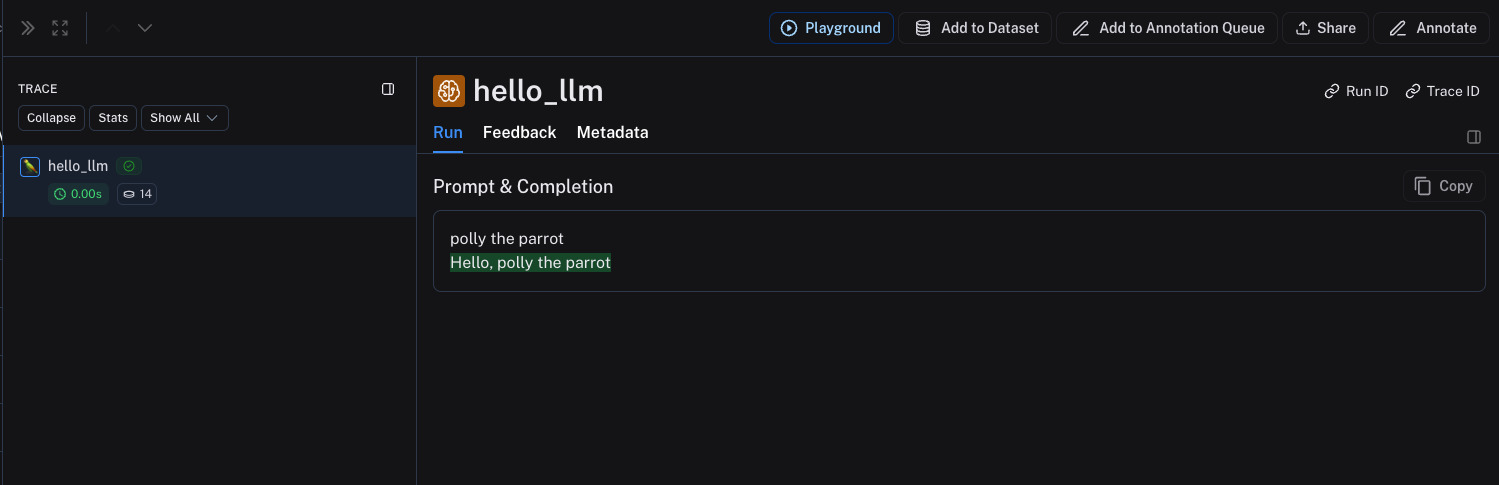
Instruct-style models
For instruct-style models (string in, string out), your inputs must contain a key prompt with a string value. Other inputs are also permitted. The output must return an object that, when serialized, contains the key choices with a list of dictionaries/objects. Each must contain the key text with a string value.
The same rules for metadata and usage_metadata apply as for chat-style models.
- Python
- TypeScript
@traceable(
run_type="llm",
metadata={"ls_provider": "my_provider", "ls_model_name": "my_model"}
)
def hello_llm(prompt: str):
return {
"choices": [
{"text": "Hello, " + prompt}
],
"usage_metadata": {
"input_tokens": 4,
"output_tokens": 5,
"total_tokens": 9,
},
}
hello_llm("polly the parrot\n")
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
const helloLLM = traceable(
({ prompt }: { prompt: string }) => {
return {
choices: [
{ text: "Hello, " + prompt }
],
usage_metadata: {
input_tokens: 4,
output_tokens: 5,
total_tokens: 9,
},
};
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "hello_llm", metadata: { ls_provider: "my_provider", ls_model_name: "my_model" } }
);
await helloLLM({ prompt: "polly the parrot\n" });
The above code will log the following trace: