Version datasets
In LangSmith, datasets are versioned. This means that every time you add, update, or delete examples in your dataset, a new version of the dataset is created.
Create a new version of a dataset
Any time you add, update, or delete examples in your dataset, a new version of your dataset is created. This allows you to track changes to your dataset over time and to understand how your dataset has evolved.
By default, the version is defined by the timestamp of the change. When you click on a particular version of a dataset (by timestamp) in the "Examples" tab, you can see the state of the dataset at that point in time.
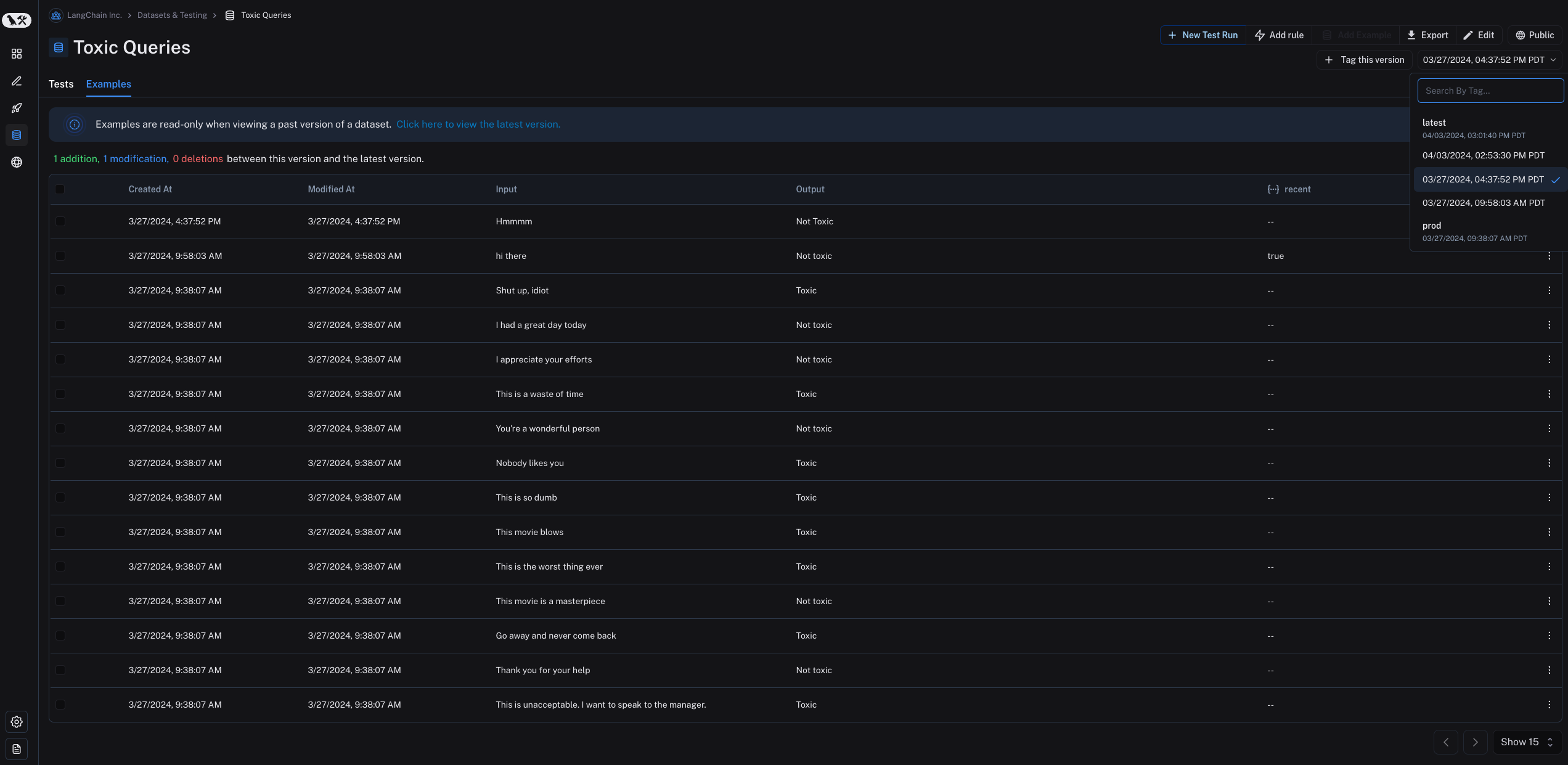
Note that examples are read-only when viewing a past version of the dataset. You will also see the operations that were between this version of the dataset and the "latest" version of the dataset. Also, by default the latest version of the dataset is shown in the "Examples" tab and experiments from all versions are shown in the "Tests" tab.
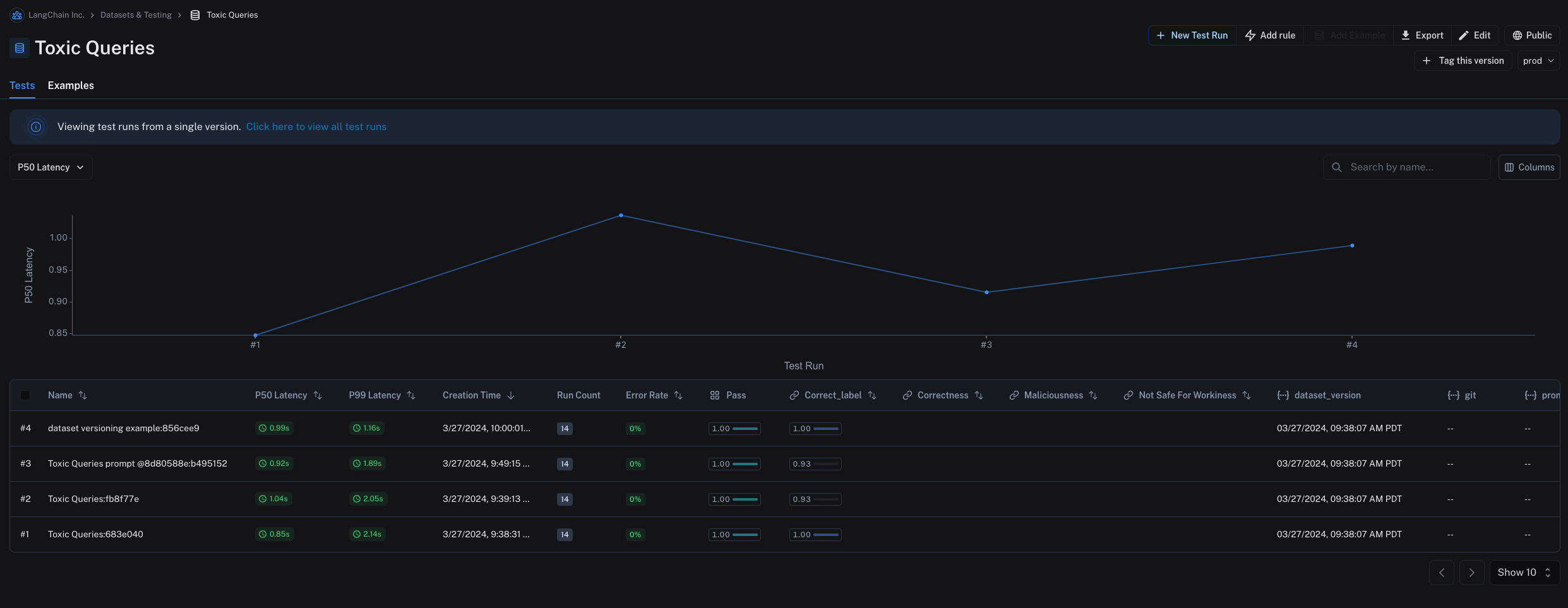
In the "Tests" tab, you can see the results of tests run on the dataset at different versions.
Tag a version
You can also tag versions of your dataset to give them a more human-readable name. This can be useful for marking important milestones in your dataset's history.
For example, you might tag a version of your dataset as "prod" and use it to run tests against your LLM pipeline.
Tagging can be done in the UI by clicking on "+ Tag this version" in the "Examples" tab.
You can also tag versions of your dataset using the SDK. Here's an example of how to tag a version of a dataset using the python SDK:
from langsmith import Client
fromt datetime import datetime
client = Client()
initial_time = datetime(2024, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0) # The timestamp of the version you want to tag
# You can tag a specific dataset version with a semantic name, like "prod"
client.update_dataset_tag(
dataset_name=toxic_dataset_name, as_of=initial_time, tag="prod"
)
To run an evaluation on a particular tagged version of a dataset, you can follow this guide.